
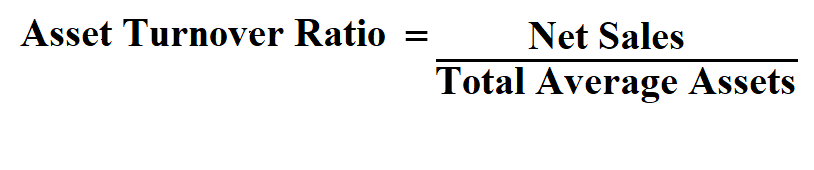
We understood how to calculate the fixed asset coverage ratio and covered an example for more understanding. In general, the higher the fixed asset turnover ratio, the better, as the company is implied to be generating more revenue per dollar of long-term assets owned. Financial ratios are created with the use of numerical values taken from financial statements to gain meaningful information about a company. And after this, you need to divide the remaining value with the total debt of the company. With the current ratio it is not the case of the higher the better, as a very high current ratio is not necessarily good.Īfter doing this, you need to minus the total asset with the total current liability that you calculated using the formula. These ratios are sometimes known as risk ratios, positioning ratios or solvency ratios. Ideally, the capex is higher than the depreciation expense to replenish old assets.Gearing relates to an organisation’s relative levels of debt and equity and can help to measure its ability to meet its long-term debts. Company B’s reinvestment ratio of less than 1 is worrisome. Company A also has a higher reinvestment ratio indicating the business is replacing its old assets effectively. This indicates a comparatively lower “ageing asset base” against Company B. It also has a higher Capex ratio than Company B, indicating higher potential future growth. This indicates that for every $1.00 spent on fixed assets, it generates higher sales (0.5 against 0.45). Both companies operate in similar industries making comparisons reasonable.Ĭompany A has a higher fixed asset turnover ratio than Company B. We can better understand asset ratios using information from two companies with similar sales but differences in asset-related figures. This would suggest that the business is not replacing old assets.Īverage Age Ratio = Capital Expenditure / Depreciation Asset Ratios Example Depreciation is calculated at historical costs so should be a cause for concern if this ratio was hovering close to 1. Due to inflation, assets purchased many years ago will cost more to replace than if purchased today. In other words, are depreciating assets being replaced? This ratio is expressed as a multiple and a healthy business should expect this multiple to be greater than 1. It is an indicator of what level of investment is being made into assets. The reinvestment ratio (sometimes referred to as the replenishment ratio) compares Capex to depreciation. A high ratio would suggest that much of the asset’s life has already been used, and the business faces an “ageing asset base”, which will require investment.Īverage Age Ratio = Accumulated depreciation / Gross PP&E Reinvestment Ratio By measuring accumulated depreciation relative to the gross value of the asset, we can see how “old” the asset is as a percentage of its total life. The average age ratio appraises the age of the asset (in this case, PP&E) and shows the average age of assets. This pattern of continuous reinvestment of retained earnings year after year is what drives company growth andĬapex Ratio = Capital expenditures / Sales Average Age of PP&E If a company continues to invest in resources through increase in capital expenditure, then we would expect to see an increase in sales the future. An increase in this ratio overtime would suggest future growth. The capex ratio measures investments in PP&E relative to company sales. The ratio is lower for asset-intensive industries such as telecommunications or utilities.įixed Asset Turnover = Sales / Net fixed assets Capex Ratio The ideal asset turnover ratio varies by industry. Analysts should keep an eye on any significant asset purchases or disposals during a year as these can impact the asset turnover ratio. A high asset turnover ratio indicates greater efficiency to generate sales from fixed assets. It assesses whether a company is investing wisely in its assets. This ratio measures the efficiency of a company’s PP&E in generating sales. It indicates whether depreciating assets are being replaced.įixed Asset Ratios – Explained Fixed Asset Turnover The reinvestment ratio (sometimes referred to as the replenishment ratio) compares capex to depreciation.A high ratio suggests the business has an “ageing asset base” The average age ratio appraises the age of the asset base (in this case PP&E) and shows the average age of assets.An increase in this ratio over time may suggest future growth. The Capex ratio measures investments relative to company sales.A higher fixed asset turnover indicates greater efficiency in generating sales from fixed assets. Fixed asset turnover measures the efficiency of PP&E in generating sales.Four commonly used asset ratios are: Fixed asset turnover, Capex ratio, the average age of PP&E, and the reinvestment ratio.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
